As we approach the end of the calendar year 2020 and head into the information reporting compliance season that begins in January 2021, information return filers[1] need to be aware of changes that will require adjustment to their usual compliance procedures. Below, we examine some big changes for reportable payments made in the calendar year 2020.
The PATH Act
The Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes Act of 2015 (“PATH Act”) changed the due date for Forms 1099-MISC reporting nonemployee compensation (“NEC”) in box 7. Beginning with payments made in the calendar year 2018 (information returns filed in 2019), the new deadline for filing such returns with the IRS and furnishing the recipient copy was advanced to January 31. The reporting deadline for Forms 1099-MISC reporting other types of payments remained February 28 (or March 31 for returns filed with the IRS electronically).
NEC includes payments made in the course of a trade or business for services performed by a payee who is not the payer’s employee. Such payees may include independent contractors, vendors, and professional service providers, including payments to attorneys for legal services.
The PATH Act also eliminated the automatic 30-day extension to file information returns reporting NEC. Instead, only a non-automatic extension is available, but only under the following enumerated circumstances:
- The payer business suffered a catastrophic event in a Federally Declared Disaster Area that made the business unable to resume operations or made necessary records unavailable;
- Fire, casualty, or natural disaster affected the operation of the business;
- A death, serious illness, or unavoidable absence of the individual responsible for filing the information returns affected the operation of the business;
- The information return is being filed for the first year the business was established; or
- The filer did not receive timely data on a third-party payee statement. This statement might be a Schedule K-1, “Partner’s Share of Current Year Income, Deductions, Credits, and Other Items,” Form 1042-S or the statement of sick pay required under Reg. § 31.6051-3(a)(1). In this case, the extension will be granted even if the filer receives the statement by the statutory furnished deadline, provided that the filer did not receive the statement in time to prepare an accurate information return.
New Forms 1099-NEC & 1099-MISC for 2020 and Due Dates
The bifurcation of the information reporting deadline and elimination of the automatic extension under the PATH Act caused much confusion and noncompliance, the consequences of which can prove substantial (see below, “Income Matching and Information Reporting Penalties”).
Effective for payments made in the calendar year 2020, the IRS has created a new form for reporting NEC – Form 1099-NEC. For information return filings starting in 2021 (for the calendar year 2020 payments), this new Form 1099-NEC will be used to report NEC that was previously reported on Form 1099-MISC in box 7.
The due date for filing Form 1099-NEC with the IRS and mailing copies to recipients is January 31. Since January 31, 2021 is a Sunday, the 2021 due date is Monday, February 1, 2021.
The due date for filing Forms 1099-MISC with the IRS is February 28 (or March 31, if applicable), while recipient copies must be mailed by January 31 (February 1, 2021 for 2020 payments).
Please see the full list of information returns and due dates here.
Note: Form 1099-MISC has also been revised for 2020, including the reassignment of the types of payments and income reported in certain boxes! Make sure that you re-map your payment data accordingly.
Income Matching and Information Reporting Penalties
The IRS relies on “information-at-the-source,” including information returns such as Forms 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC, to ensure taxpayers comply with the tax laws and pay their fair share of taxes. There is a punitive penalty scheme to enforce compliance. If the IRS doesn’t receive timely and accurate information about payments payers make, it doesn’t have the data necessary for one of its benchmark programs designed to ensure compliance – income matching (also known as document matching).
The IRS’ income matching program is designed to match income reported by a payer on an information return with income reported on the recipient payee’s tax return. If income is omitted or otherwise doesn’t match what was reported on the information return, the IRS will issue an automated notice to the payee to resolve the discrepancy.
Under IRC § 6721, payers that file information returns (such as Forms 1099-NEC and 1099-MISC) are subject to penalties if such information returns are incorrect. The “failures” that may lead to a proposed penalty assessment are:
- Failure to file;
- Filed with missing/incorrect TIN (or other missing or incorrect information);
- Filed untimely;
- Filed on paper when electronic filing was required; or
- Filed in an incorrect format
Several factors determine the applicable penalty, including whether the failure was due to “intentional disregard” and, if a correction was filed, when such correction was filed. The penalty scheme for payments made in 2020 subject to information reporting in 2021 is:
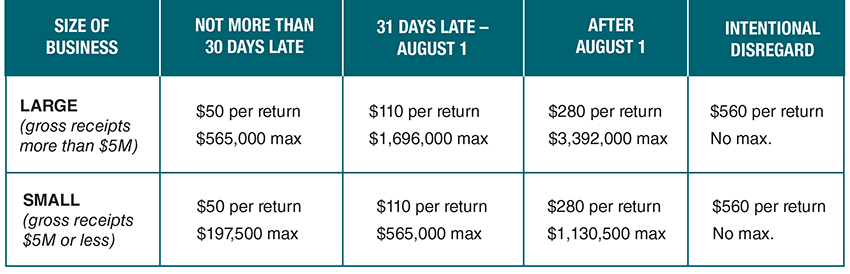
The IRS may also assess the penalty a second time under IRC § 6722 for failure to furnish correct payee statements. For example, if an information return is filed late with the IRS and the payee statements is likewise furnished late, the filer can be subject to the penalties under both IRC §§ 6721 and 6722.
Many information return filers are not aware that, with some exceptions, these penalties are not discretionary – they will be automatically proposed if there are failures. The IRS proposes these penalties by issuing Notice 972CG, “Notice of Proposed Civil Penalty” to filers.
____________________________________
[1] In this article we refer to “payers” and “filers.” These terms refer to all of the payers of payments in the United States that – in the course of a trade or business – make payments subject to the information return reporting rules of the Internal Revenue Code (“IRC”) and the related Untied States Treasury Regulations. Not for profit organizations, trade organizations, public agencies and other organizations are subject to these rules, as are for-profit businesses and individuals engaged in a trade or business.
Note: This information was provided by Miller Kaplan.
